A breast surgeon discusses the best practices for breast cancer surgery during the COVID-19 pandemic.

A breast surgeon discusses the best practices for breast cancer surgery during the COVID-19 pandemic.

Although cancer screening rates and ensuing diagnoses dropped significantly during the height of the COVID-19 pandemic, testing rates from June 2020 through September 2020 have nearly returned to pre-pandemic levels.

Novel therapeutics have not only boosted outcomes in myelofibrosis, but paved the way for new combination treatment strategies, too.

Minimal residual disease has helped to predict relapse in numerous leukemia subtypes, with novel testing methods helping to identify the biomarker at a higher sensitivity than ever before.

Health-related quality of life was maintained for patients with EGFR-positive non–small cell lung cancer who received treatment with adjuvant osimertinib.

Mean daily step count during the first 2 weeks of treatment with SM-88 (racemetyrosine) was found to correlate with overall self-reported quality of life (QoL) in patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer.
The reversible BET inhibitor CC-90010 was found to have preliminary antitumor activity in patients with heavily pretreated, advanced solid tumors and relapsed/refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma.

Patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia who received treatment with single-agent acalabrutinib experienced a low incidence of cardiac toxicities leading to treatment discontinuation.

The advent of 3D printing has led to an exciting revolution in limb salvage surgery for patients with bone tumors and soft tissue sarcomas, and have resulted in more precise resection and high-fidelity reconstruction, according to R. Lor Randall, MD, FACS.
Ursula Matulonis, MD, highlights immunotherapy agents have demonstrated moderate clinical activity for patients with gynecologic cancers, however they fail to yield significant response rates in both the newly-diagnosed and recurrent settings.

Beyond single-agent chemotherapy, few effective treatment options are available for metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), according to Candace Mainor, MD, but several approaches comprised of immunotherapy, antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), and PARP inhibitors are shifting standards of care and eliciting impressive response rates in heavily pretreated patients.

To address such disparities, it is important for institutions to embrace and promote the fostering of an inclusive culture and environment for health care professionals of all races and genders, and to adequately equip women specifically with the tools they need to achieve success in the field.
Germline genetic testing is a key component of prostate cancer treatment, and broader testing criteria combined with reduced barriers to these tests could result in better informed care, including preventive surveillance, according to data from a recent study.

Clinical cancer trials that fail to successfully enroll a racially and ethnically diverse patient population run the risk of leaving critical gaps in understanding regarding the effectiveness of new approaches. The importance of inclusion in such efforts is underscored even further as more studies demonstrate race-based differences in relation to immune status, incidences of tumor mutation, and even mortality rate in patients with cancer.

Racial and ethnic disparities in cancer clinical trials has a pressing challenge that not only impacts diagnostics and treatment of minority populations, but also raises the question of whether trial results are truly applicable across all populations, according to Ruben Mesa, MD.

Telehealth is likely to stay in the oncology realm, even after the novel coronavirus 2019 pandemic passes.

Although pancreatic cancer has been a historically difficult disease to treat, the emergence of novel combinations have allowed for more patients to receive later lines of therapy, and recent advances have inspired a shift to more personalized treatment approaches to improve outcomes, according to Syma Iqbal, MD.

One of the most important tasks that oncology nurses face is ensuring that patients are taking their medications consistently and correctly, and that adverse events (AEs) are properly managed—specifically in those patients with breast cancer, according to Patricia Jakel, RN, MN, AOCN.
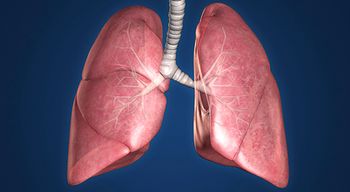
An Emory University-led phase 2 study will evaluate whether the the PI3K-gamma/delta inhibitor duvelisib is effective at reducing lung inflammation in patients with severe novel coronavirus 2019.

Patients with MDS/MPN unclassifiable, whose genes were found to be the most heterogeneous, had a different molecular landscape that was comparable with those observed within other MDS/MPN.

Treatment with the BTK inhibitor acalabrutinib resulted in decreased inflammation and improve outcomes in patients with severe COVID-19.

Only a small percentage of patients with kidney cancer who are considered to be particularly vulnerable to COVID-19 have actually been tested for infection.

During his presentation, Michael A. Postow, MD, briefly reviewed the latest updates with immunotherapy and other targeted treatments in melanoma reported during the 2020 ASCO Virtual Scientific Program.