Articles by Jessica Hergert
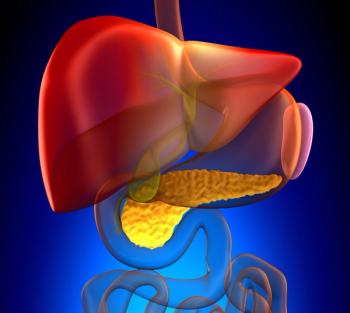
Although the combination of atezolizumab and bevacizumab has become the standard frontline treatment for patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma, whether immunotherapy could play a role in earlier lines of treatment remains the subject of ongoing research.
First-line treatment with camrelizumab, an investigational PD-1 inhibitor, plus chemotherapy induced robust and durable clinical responses in patients with advanced squamous non–small cell lung cancer.
Namrata (Neena) Vijayvergia, MD, discusses the emerging role of immunotherapy in resectable and metastatic esophageal and gastric cancers, as well as key nuances that could complicate these agents’ utility in clinical practice.

The real-world utilization of axicabtagene ciloleucel demonstrated favorable outcomes and less frequent toxicity events compared with those reported in the pivotal ZUMA-1 trial and other real-world studies.

Immunotherapy continues to improve upon the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer, and there are more exciting advancements on the horizon.

“We should never be complacent; we should never be skeptical,” said Lilenbaum. “We need to continue to pursue new treatments, and if nothing else, the past 2 decades are a testament to how we can actually make a difference in the natural history of the disease by appropriate interventions.”

Although lung-sparing lung nodule resection in the form of lesser resection is available to some patients with lung cancer, it is critical to tailor surgical interventions based on pathologic assessment results, said Henning Gaissert, MD, who added that utilizing a multimodal approach to treatment can help alleviate some of the burden of treatment selection.
“Second-line maintenance therapy is going to be incredibly important for patients because we know that once a patient with ovarian cancer recurs, their disease is incurable."

CAR T-cell therapy may change the treatment paradigm for relapsed/refractory myeloma.
Robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy was shown to achieve early return of urinary continence without a negative impact on complications and cancer outcomes among men with localized prostate cancer.

Longer-term data demonstrated that treatment with the radiopharmaceutical Lutathera (lutetium-177 dotatate) continued to show low rates of toxicity among patients with somatostatin receptor–positive neuroendocrine tumors (NETs), said Edward M. Wolin, MD, who added that the positive findings open the potential for novel combinations with the agent.
Findings from the noncomparative, phase 2, biomarker-driven BIONIKK trial demonstrated clinical evidence to support the use of molecularly-directed frontline therapy as means to enrich responses in patients with metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC).
The novel VEGFR, FGFR, and CSF-1R inhibitor surufatinib yielded a statistically significant and clinically meaningful progression-free survival (PFS) benefit compared with placebo in patients with advanced pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (pNETs), according to results from the randomized phase 3 SANET-p trial that were presented virtually during the 2020 ESMO Congress.

The advent of immunotherapy has revolutionized multiple areas of cancer treatment, said Timothy Cragin Wang, MD, who added that the transformative potential of the modality has been mild at best in the field of colorectal cancer (CRC).

Investigational CAR T-cell therapy products have demonstrated unprecedented responses rates with seemingly durable remissions in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma, explained Luciano J. Costa, MD.
The novel multimodal FirstSightCRC test has shown promise in identifying colorectal cancer (CRC), as well as precancerous polyps and advanced adenomas, said Shai Friedland, MD, who added that results from the blood-based assay can inform whether a patient should undergo a colonoscopy.
Lurbinectedin (Zepzelca) was added to the Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) on July 7, 2020 for the treatment of patients with small cell lung cancer (SCLC), according to a press release from Jazz Pharmaceuticals.
Five-year findings from the phase 3 COMBI-AD trial revealed that the combination of dabrafenib (Tafinlar) and trametinib (Mekinist) led to sustained long-term relapse-free survival (RFS) benefit compared with placebo for patients with resected, stage III BRAF V600E/K–mutant melanoma, said Axel Hauschild, MD, PhD.
The addition of immunotherapy to the triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) armamentarium has led to a paradigm shift and sparked an abundance of research with immuno-oncology (IO) drugs in new combinations and settings, explained Hope S. Rugo, MD.

The implementation of a multidisciplinary team, which has demonstrated a marked survival advantage compared with single-provider care, is critical in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), particularly as it relates to the evolving role of radiation, surgical resection, liver transplantation, and systemic treatment, explained Neehar Parikh, MD.

A number of treatment options exist for patients with localized hepatocellular carcinoma, including surgical resection, transplantation, ablation, stereotactic body radiotherapy,, and embolization.

Combined treatment with brentuximab vedotin and nivolumab could provide a more tolerable option for older patients with classical Hodgkin lymphoma.

CAR T-cell therapy is poised to have a significant impact on the treatment of patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma, says Nina Shah, MD.
T-cell therapies, such as tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte (TIL) therapy, T-cell receptor (TCR) therapy, and CAR T-cell therapy, which have shown preliminary signals of activity, are poised to have a dramatic impact in metastatic melanoma, according to Jason J. Luke, MD, FACP.
The optimal sequencing of therapies for patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) has proven to be a significant clinical challenge following the approvals of additional agents, said William K. Oh, MD.
After nearly 4 decades of stagnation, the advent of immunotherapy has transformed the frontline treatment paradigm for patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC). However, biomarkers are needed to better inform which patients are most likely to respond to checkpoint inhibitors, said Jason Niu, MD, PhD.

A flood of targeted therapy and immunotherapy options to both the first- and second-line settings of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has had significant implications on the treatment of patients in this space and will likely create challenges regarding sequencing, said Richard S. Finn, MD.

Nearly 1 year following the first checkpoint inhibitor approval in advanced triple-negative breast cancer, additional immunotherapeutic agents are poised to enter the field, according to Rita Nanda, MD.
With the advent of targeted therapy, understanding the genetic components of a patient's disease has become critical in oncology. As the role of genetic testing in prostate cancer has grown, the field is also overcoming hurdles with making it more widespread, said Thomas J. Polascik, MD.
The role of radical surgical resection in advanced melanoma has become more conservative and cosmetically sensitive, according to Richard L. Shapiro, MD.




























