
Finding ways to prevent and manage stress may be key to optimizing clinical outcomes in oncology.

Finding ways to prevent and manage stress may be key to optimizing clinical outcomes in oncology.

Electronic patient-reported outcomes may have a place in high-quality cancer care, according to investigators.

Pembrolizumab, in addition to enzalutamide and androgen deprivation therapy, was not associated with better radiographic progression-free survival outcomes in patients with metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer.
Olaparib did not significantly improve overall survival compared with chemotherapy in recurrent, platinum-sensitive ovarian cancer.

A phase 3 trial based out of India suggests that olanzapine may be useful in reducing chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting.
The median overall survival with niraparib, abiraterone acetate, and prednisone was 30.4 months vs 28.6 months with abiraterone acetate and prednisone alone.
The duration of response was 39.2 months among patients with 1 metastatic site treated in the combination arm vs 29.5 months for patients given sunitinib.
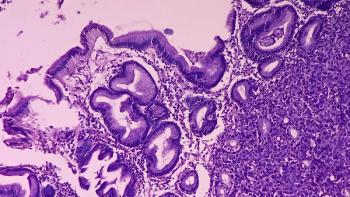
The median progression-free survival with cabozantinib was 8.3 months vs 3.2 months with placebo among patients with extra-pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors.

Patients who received amivantamab plus lazertinib and chemotherapy achieved a median progression-free survival of 8.3 months.
The median progression-free survival was not reached with atezolizumab plus chemotherapy vs 6.9 months in the placebo group of patients with advanced or recurrent endometrial cancer.

The median radiologic progression-free survival was 12.02 months in the 177Lu-PSMA-617 group vs 5.59 months in the androgen receptor pathway inhibitor change group.

Datopotamab deruxtecan improved progression-free survival in select subsets of patients with advanced or metastatic non–small-cell lung cancer.

Patients with metastatic hormone receptor-positive breast cancer treated with datopotamab deruxtecan experienced a statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvement in progression-free survival.

Sotorasib plus panitumumab showed consistent efficacy across key subgroups of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer.
The 12-month overall survival rates were 48.7% and 35.3% with tisotumab vedotin and chemotherapy, respectively, among patients with recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer.

Nivolumab plus gemcitabine-cisplatin improved overall and progression-free survival in unresectable or metastatic urothelial carcinoma.
For the first time, a new therapeutic regimen outperformed chemotherapy in improving overall survival in frontline urothelial cancer.

Durvalumab plus first-line chemotherapy, followed by maintenance treatment with durvalumab plus olaparib, emerges as a potentially effective combination for patients with limited treatment options.

In the intention-to-treat population, the median progression-free survival was 24.8 months with selpercatinib vs 11.2 months.

The median progression-free survival was not reached with selpercatinib vs 16.8 months with other kinase inhibitors.

Adjuvant alectinib significantly improved disease-free survival in patients with ALK-positive, early-stage, non–small-cell lung cancer.

Treatment with neoadjuvant nivolumab, followed by adjuvant nivolumab after surgery, led to significantly improved event-free survival in the first phase 3 perioperative study in patients with resectable non-small cell lung cancer.
Tarlatamab induced a 40% objective response rate among patients with pretreated small cell lung cancer—including many patients who had already received 3 lines of therapy.

Using established guidelines to monitor and intervene early for diarrhea and neutropenia may result in longer treatment durations and sustained benefit from sacituzumab govitecan.

Neratinib was associated with a clinical benefit rate of 45.5% among patients with metastatic or recurrent HER2-mutated cervical cancer.

Derazantinib, an FGFR inhibitor, was associated with a median progression-free survival (PFS) of 7.8 months in patients with FGFR2-positive intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.

Neoadjuvant cemiplimab elicited promising pathologic complete responses in patients with cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma.
For patients receiving an aromatase inhibitor for hormone receptor–positive, HER2-negative breast cancer, the addition of abemaciclib doubled median progression-free survival vs placebo.

Sotorasib doubled the progression-free survival rate in patients with KRAS G12C–mutated non–small cell lung cancer.

Julie Malo, CCRP, a research nurse with the University of Montreal, discusses a nurse-directed initiative examining how the gut microbiome affects immune checkpoint blockade responses in patients with non–small cell lung cancer.