
Dostarlimab-gxly has been granted regular approval for the treatment of patients with dMMR endometrial cancer. The label comes with warnings for immune-mediated adverse effects.

Dostarlimab-gxly has been granted regular approval for the treatment of patients with dMMR endometrial cancer. The label comes with warnings for immune-mediated adverse effects.

The National Comprehensive Cancer Network has updated their guidelines to include neratinib for patients with HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer.

Patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma continued to displayed a survival benefit with pembrolizumab at a 4-year follow-up.

A study in the Oncology Nursing Forum highlights which factors are associated with positive psychology and symptom burden in colorectal cancer survivors.

Findings from a phase 2/3 trial found better disease-free and overall survival outcomes with radiation plus docetaxel vs radiation alone in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
Patients with RAS-wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer did not experience a benefit in terms of response rate or survival when cetuximab was added to the first cycle of chemotherapy.
Nanvuranlat inspired better progression-free survival in patients with advanced, pretreated refractory biliary tract cancer, meeting the primary end point of a phase 2 trial.
Newer agents approved for frontline hepatocellular carcinoma, including lenvatinib, and atezolizumab/bevacizumab, yielded superior survival outcomes than sorafenib in a real-world setting.

At 11.3 months of follow-up, magrolimab, rituximab, gemcitabine, and oxaliplatin yielded an overall response rate of 51.5%, including a complete response rate of 39.4%, among patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.

The FDA has approved sacituzumab govitecan-hziy for patients with unresectable locally advanced or metastatic hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer.

Research published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology seeks to inform best practices in establishing smoking cessation programs across cancer care centers.

First-line ibrutinib plus prednisone missed the primary endpoint in the phase 3 iNTEGRATE trial by not improving the response rate in patients with chronic graft-versus-host-disease compared with placebo plus prednisone.

Although most patients in the real-world setting would not have met the clinical trial eligibility criteria, the efficacy and safety outcomes with idecabtagene vicleucel were similar for both sets of patients with multiple myeloma.

Each month, Oncology Nursing News® takes a look back at our most popular stories.

Nilesh Kalariya, PhD, AGPCNP-BC, AOCNP; and Laura J. Zitella, MS, RN, ACNP-BC, AOCN, discuss practice-changing presentations from the 64th American Society of Hematology Annual Meeting and Exposition.

Neoadjuvant pembrolizumab elicited high clinical activity in patients with mismatch repair deficiency/microsatellite instability high solid tumors and was well tolerated.

Reanne Booker, MN, NP, shares how nurses can increase patient understanding on the role of palliative care in oncology.
January is cervical cancer awareness month. This fourth article in a series underscores the role of the nurse or social workers in patient advocacy.

Patients with hepatocellular carcinoma experienced better health-related quality of life outcomes with tislelizumab vs sorafenib.
Encorafenib plus cetuximab, along with chemotherapy, was linked to antitumor activity and a manageable safety profile in patients with BRAF V600E-mutant metastatic colorectal cancer.

The FDA has granted an accelerated approval to elacestrant (Orserdu) for the treatment of patients with estrogen receptor–positive, HER2-negative advanced or metastatic breast cancer following at least 1 prior lines of endocrine therapy.

Pirtobrutinib has been approved for patients with mantle cell lymphoma. The prescribing label comes with warnings for infections, hemorrhage, cytopenias, atrial fibrillation and flutter, second primary malignancies, and embryo-fetal toxicity.

Neoadjuvant chemoradiation followed by pancreaticoduodenectomy resulted in 0.14 more quality-of-life years than upfront surgery followed by adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with resectable pancreatic cancer.
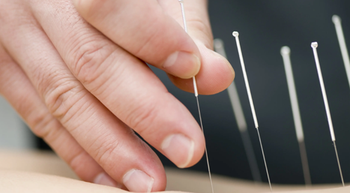
Heather Jackson, PhD, FNP-BC, NEA-BC, FAANP, provides a case-based perspective on the benefit of auricular acupuncture as a tool for managing cancer pain.

Pembrolizumab has been approved by the FDA as an adjuvant treatment for patients with stage IB, II, or IIIA following resection and platinum-based chemotherapy.
Findings from the phase 3 SUNLIGHT study showed that adding bevacizumab to trifluridine/tipiracil boosted overall survival in metastatic colorectal cancer.

Investigators identified underrepresentation and imbalances in demographic and geographic representation in clinical trials leading to FDA approvals.

Patients with breast cancer who carry BRCA1, BRCA2, CHEK2, or PALB2 germline pathogenic variants may be at a greater risk for contralateral breast cancer and may benefit from enhanced surveillance and risk-reduction strategies.

The median overall survival with frontline liposomal irinotecan/NALIRIFOX was 11.1 months vs 9.2 months with nab-paclitaxel plus gemcitabine in patients with metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
The median overall survival with nivolumab plus chemotherapy was 12.8 months, vs 10.7 months with chemotherapy alone, in patients with treatment-naïve advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.