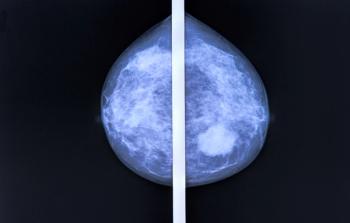
CDK4/6 inhibitors have demonstrated promise in treating patients with estrogen receptor (ER)–positive, HER2-negative breast cancer in both a neoadjuvant and adjuvant setting.
Caroline Seymour joined MJH Life Sciences in 2018 and has expertise in video production and print/digital publication. Email: cseymour@onclive.com

CDK4/6 inhibitors have demonstrated promise in treating patients with estrogen receptor (ER)–positive, HER2-negative breast cancer in both a neoadjuvant and adjuvant setting.
Patients with multiple myeloma are potentially at greater risk of developing severe COVID-19 after the SARS-COv-2 vaccination induced suboptimal antibody response.

Data from a 5-year follow-up study confirmed that CPX-351 continues to be associated with long-term remission and improved overall survival compared to 7+3 chemotherapy in certain older patients with acute myeloid leukemia.
The combination of drugs resulted in a response from more than half of patients.

The phase 3 SIMPLIFY 1 and SIMPLIFY 2 trials reported that Week 24 transfusion independence resulted in an improved overall survival for patients with myelofibrosis.

The FDA has granted a breakthrough therapy designation to teclistamab for the treatment of patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma.

Age was associated with overall survival and the time to Richter transformation in adolescent and young adult patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia, according to findings from a single-institutional, retrospective study.
Molecular testing is more essential than ever, thanks to the targeted therapy options for non-small cell lung cancer.

An expert gives an overview of recent advancements in the lung cancer space.
Robert Wenham, MD, MS, FACOG, FACS, discusses the basis for combining chemotherapy, PARP inhibitors, and VEGF inhibitors with immunotherapy in ovarian cancer and ongoing research with ADCs in the field.

Tony Philip, MD, provides insight into the utility of ctDNA in the early-stage setting, trials that could determine its role in clinical practice, and detailed the shift toward nonoperative and less-intensive interventions in the early-stage and advanced settings, respectively.
Olaparib and talazoparib didn't show statistically significant improvements in overall survival compared with chemotherapy in certain patients with metastatic breast cancer. However, the results are unlikely to affect the drugs’ utility in practice, given that both agents continue to show favorable tolerability and disease control.

The KATHERINE, FeDeriCa, DESTINY-Breast01, and HER2CLIMB trials have changed practice for patients with HER2-positive breast cancer for the better.

Since the publication of the pivotal ELIANA trial in pediatric patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia, the field of CAR T-cell therapy has grown significantly and left providers better equipped to understand and manage treatment-related adverse effects, such as cytokine release syndrome.

Sapanisertib failed to show significant activity and a favorable toxicity profile in patients with refractory metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) regardless of mTOR or PTEN status.

Combinations of JAK inhibitors and novel agents, such as epigenetic regulators, could help prolong survival in patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms.
The radiographic and pathologic responses that have been seen with checkpoint inhibitors in lung cancer bodes well for the use of neoadjuvant therapy. However, the relationship between response and long-term outcomes, specifically with regard to overall survival, will have to be teased out before they become standard practice, explained David Spigel, MD.

Survival for patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) remains poor, and although immunotherapy has been positioned as a holy grail, it would be preemptive to predict its future based on the number of small studies that have been performed to date, according to Amer Zeidan, MD, MHS.

“But our study is pointing to new genes to consider. For example, we found that the BRCA2 gene, typically associated with adult breast and ovarian cancer, may also somehow influence the susceptibility of pediatric RMS.”
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has become another potential complication for patients with lung cancer, said Mark G. Kris, MD, who added that although the pandemic has disrupted patient care, it has yet to stunt scientific collaboration.

Cemiplimab (Libtayo) demonstrated clinically meaningful antitumor activity, including durable responses, and acceptable safety in patients with metastatic basal cell carcinoma (mBCC) after progression on or intolerance to hedgehog inhibitors.
Chemoimmunotherapy regimens are showing promise in the treatment of SCLC.

TP53 was found to be the only gene with a germline de novo pathogenic or likely pathogenic variant in pediatric patients with osteosarcoma, according to findings from the Children’s Oncology Group that were published in JCO Precision Oncology.
Clinical trials should not be viewed as a last resort for patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer, explained Allyson Ocean, MD, who added that even frontline standards of care should be considered after exhausting all available study options.
The paradigm of advanced nonsquamous non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is now one that necessitates discussions regarding the use of combination chemoimmunotherapy, combination immunotherapy, and single-agent immunotherapy, explained Jonathan Dowell, MD.
Bradley McGregor, MD, discusses some of the recent approaches that have emerged in bladder cancer and renal cell carcinoma, as well as anticipated developments in each field.
Parameters such as driver alterations, alternative methods for molecular testing, and immunotherapy-related biomarkers are gaining importance in lung cancer.

Liquid biopsy with circulating tumor DNA could help alleviate some of the challenges of tissue biopsy in prostate cancer, and in doing so, lead to a better precision medicine model in the field.

Fam-trastuzumab deruxtecan-nxki (Enhertu) could provide patients with metastatic non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who harbor HER2 exon 20 insertion mutations and high HER2 expression a more specific and less toxic treatment compared with platinum doublet chemotherapy. However, the jury is still out on whether the agent will be pursued as an alternative frontline therapy and in both patient subsets.