Revumenib Is FDA Approved for R/R NPM1-Mutant ALM
The FDA has approved revumenib for relapsed or refractory NPM1-mutated acute myeloid leukemia.
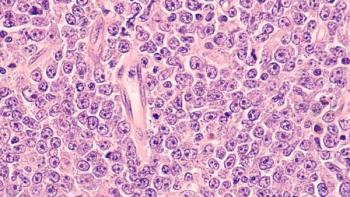
The FDA approved revumenib (Revuforj) for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients who are 1 year old and older with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with a susceptible NPM1 mutation who have no satisfactory alternative treatment options.
The drug’s effectiveness was determined in a single-arm cohort of the open-label, multicenter or AUGMENT-101 trial (NCT04065399), also known as SNDX-5613-0700, in which a susceptible mutation was confirmed in enrolled patients using next-generation sequencing or polymerase chain reaction of the last exon of NPM1.
The main outcomes of the trial were complete remission rate (CR), complete remission with partial hematological recovery (CRh), CR and CRh duration (CR+CRh) and the rate of conversion from transfusion dependence to transfusion independence.
The agency reported that CR+CRh rate was 23.1% (95% CI, 13.5-35.2) and the median CR+CRh duration was 4.5 months (95% CI, 1.2-8.1). Of the 46 patients dependent on red blood cell (RBC) and/or platelet transfusions at baseline, 8 (17%) became independent of RBC and platelet transfusions during any 56-day post-baseline period, according to the notice from the FDA.
Regarding safety, the agency noted that the drug’s prescribing information includes warnings and precautions for differentiation syndrome, QTc interval prolongation and Torsades de Pointes, and embryo-fetal toxicity.
The recommended dosage of revumenib, the agency stated, varies by a patient’s weight and concomitant use of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors.
What is Revumenib and How Does It Work to Treat AML?
Revumenib, as defined by the National Cancer Institute on its website, is a drug that binds to a protein called menin and keeps it from binding to the KMT2A protein. This, in turn, stops or slows the growth of leukemia cells with changes in the KMT2A gene.
It was previously
The oral drug was granted priority review by the FDA in June 2025 for the treatment of relapsed or refractory mutant NPM1-positive AML, according to a news release from Syndax Pharmaceuticals, the manufacturer of the drug.
Syndax announced in September that the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology for AML were updated to include revumenib as a category 2A recommendation for relapsed or refractory (R/R) acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with an NPM1 mutation (mNPM1), with the update based on positive pivotal results from the AUGMENT-101 trial of revumenib which were published in the journal Blood earlier this year.
“The inclusion of revumenib as a recommended treatment option for R/R NPM-mutated AML in the NCCN Guidelines underscores the strength of our clinical data in this population and further solidifies revumenib’s leading position,” said Nick Botwood, head of research and development and chief medical officer at Syndax, in a news release issued at the time. “Given the pivotal role NCCN Guidelines play in guiding the decision-making process for clinicians, payers, patients and other key stakeholders in the U.S. and beyond, this is a major milestone for Syndax and the entire acute leukemia community.”
Syndax has stated that additionally, multiple trials of revumenib are ongoing or planned across the treatment landscape, including in combination with standard of care therapies in newly diagnosed patients with metastaic NPM1-mutated or KMT2Ar-mutated AML.
Reference
FDA approves revumenib for relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia with a susceptible NPM1 mutation. FDA. October 24, 2025. Accessed October 24, 2025. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-revumenib-relapsed-or-refractory-acute-myeloid-leukemia-susceptible-npm1-mutation