Gastrointestinal Cancer
Latest News


Efineptakin Alfa Receives Orphan Drug Designation From FDA for Pancreatic Cancer

Camrelizumab/Chemo Combo Improves Complete Responses in Locally Advanced ESCC
Latest Videos

More News

Overall survival and progression-free survival improves with nivolumab plus chemotherapy compared with chemotherapy alone in the overall population and in patients with a PD-L1 CPS of 5 or greater.

Nivolumab plus chemotherapy enhanced overall survival and progression-free survival in patients with advanced or metastatic gastric cancer, gastroesophageal junction cancer, or esophageal adenocarcinoma.

Oncology nurses can illuminate the potential of avasopasem to enhance pancreatic cancer outcomes and champion ongoing research.

The median overall survival was 77.5 months with frontline pembrolizumab vs 36.7 months with chemotherapy in patients with microsatellite instability–high or mismatch repair–deficient metastatic colorectal cancer.

Holly Chitwood, DNP, APRN, FNP-C, AGACNP-BC, shares her real-world experience with circulating-tumor-DNA monitoring in the colorectal cancer setting.
Tammy Triglianos, DNP, ANP-BC, AOCNP, discusses optimal adjuvant treatment approaches for patients with stage III colon cancer.

The FDA has approved pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy to treat adults with locally advanced or metastatic, HER2-negative gastric cancers.

The PD-L1 IHC 22C3 pharmDx diagnostic tool will help identify patients with gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma whose disease expresses PD-L1 and who are thereby eligible for pembrolizumab.

The FDA has restricted the indication for gastric cancer to only include patients whose tumors express PD-L1 (CPS ≥ 1) as determined by an FDA-approved test.
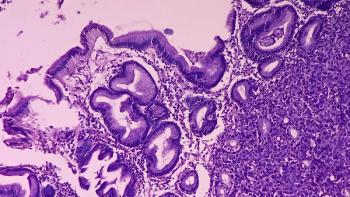
The median progression-free survival with cabozantinib was 8.3 months vs 3.2 months with placebo among patients with extra-pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors.

The FDA has approved pembrolizumab in combination with chemotherapy as a treatment for patients with locally advanced unresectable or metastatic biliary tract cancer.

Holly Chitwood, DNP, FNP-C, AGACNP-BC, explains how circulating tumor DNA monitoring helps providers screen minimal residual disease in individuals with colorectal cancer.

Sotorasib plus panitumumab showed consistent efficacy across key subgroups of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer.
Cancer screening tests may not extend life expectancy; however, they still are valuable for public health.

The approval of FoundationOne CDx as a companion diagnostic for selpercatinib seeks to broaden access to therapies for patients with RET fusion–positive solid tumors.
Nivolumab plus chemotherapy offers patients with gastric and esophageal cancers a reduced risk of symptom burden and a longer time to deterioration.

Immuno-oncology regimens were linked with improved long-term survival among patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.

Lorazepam was associated with worse survival outcomes for patients with pancreatic cancer, while alprazolam was associated with improved outcomes.
It is essential to continue to develop and incorporate educational strategies to increase screening for colorectal cancer in our communities.

Circulating tumor DNA analysis is playing an increasingly important role in colorectal cancer treatment decision-making.

The median disease-free survival with GVAX vaccine plus low-dose cyclophosphamide; GVAX plus cyclophosphamide and nivolumab; and GVAX plus cyclophosphamide, nivolumab, and urelumab, was 13.90 months, 26.1 months, and 31.6 months, respectively.

The FDA has approved the therascreen PDGFRA kit to identify patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumors who may benefit from treatment with avapritinib.

Magnetic resonance-based imaging alone was 40% accurate in positively predicting pathologic complete response in patients with rectal adenocarcinoma undergoing total neoadjuvant therapy.

A triplet regimen of trifluridine, tipiracil, and bevacizumab has been approved as a treatment for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer.

Patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma who received rivoceranib/camrelizumab achieved a median progression-free survival of 5.6 months vs 3.7 months with sorafenib.